Definitive Guide to SEO Optimisations for Your Website 🔎
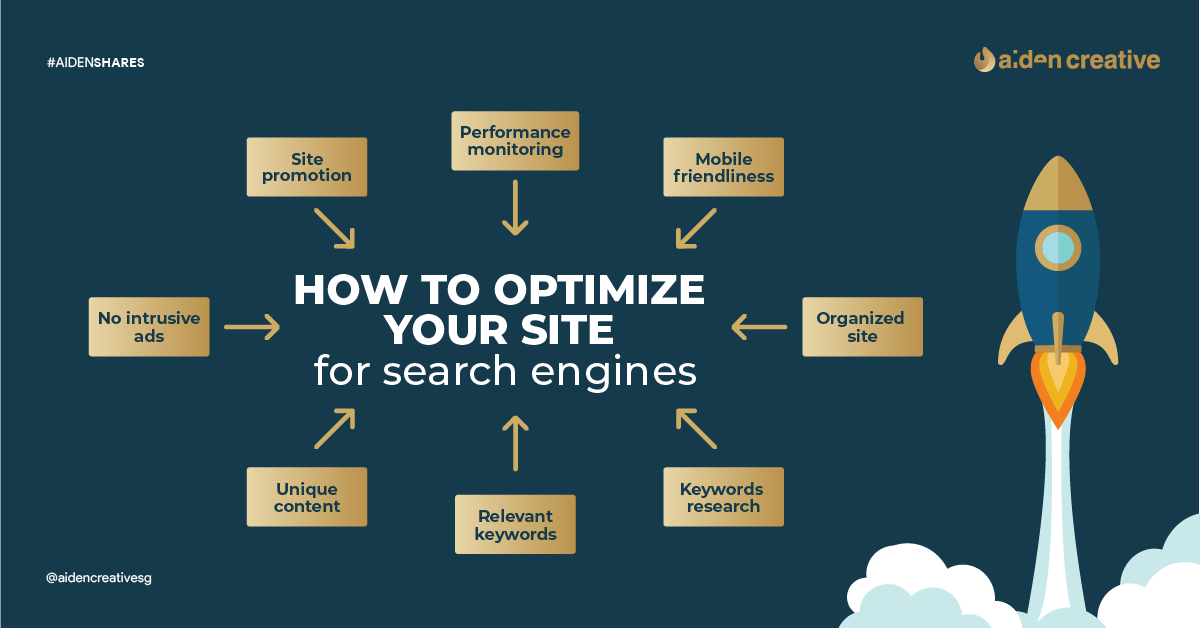
Search engine optimisation (SEO) is an essential practice in helping a website’s visibility and traffic. Building and maintaining a fully optimised website can bring positive results for the user experience of a site’s visitors and its performance in organic search results.
Through this guide, you can learn how to optimise your website through SEO best practices for all websites’ types and sizes.
SEO jargon in this guide 📚
Before we start, here is a glossary of terms in this guide:
- SEO: stands for search engine optimisation, a practice to make a site accessible to search engines and served to its users when they perform a search related to your site
- Index: a “library” where search engines store information they know about web pages; to index a site means search engines add information they get to the index
- Crawl: the process of discovering new or updated web pages and index them if deemed appropriate
- Crawler: a search engine’s software to crawl your site, for example, Googlebot from Google or Bingbot from Bing
- Technical SEO: behind the scene optimisations so crawlers can find and index your web pages
- On-page SEO: content optimisations to increase usability and user experience of a site
- Off-page SEO: employing tactics that happen outside of your website to improve organic performance
- SERP: search engine result page
- Internal link: link targeted to other pages on your site
- External link: link targeted to a page outside your site
Technical SEO optimisations 👩💻
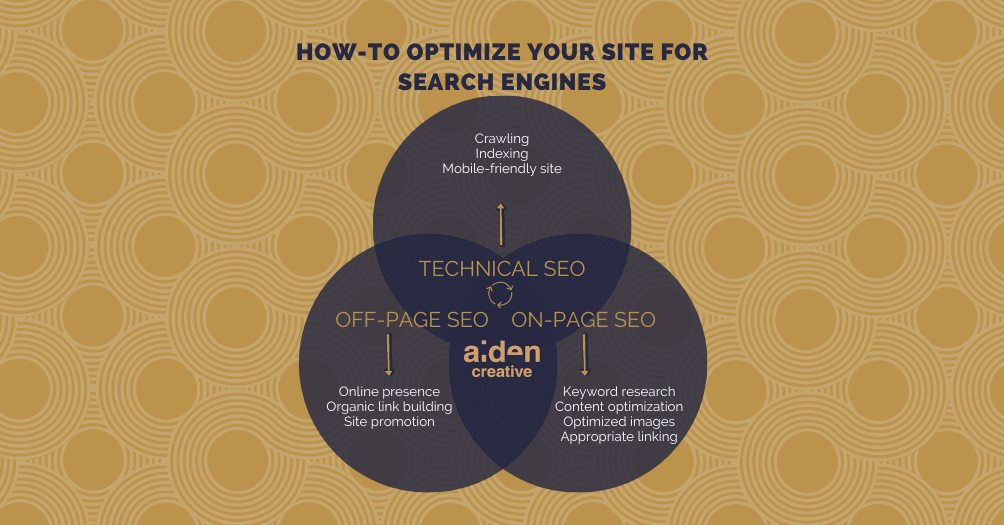
Technical SEO is crucial in a website. If your site is not in the index of search engines, it may hinder the optimisations you do on and off your site’s pages. Hence, we will start from a technical perspective. For this part, we recommend that you follow it with your web developers.
Checking whether a site is in the index or not
Perform a simple test to determine whether a homepage is in the index or not by performing a search using the “site” operator. For instance, a query of “site:www.bing.com” will yield these results on Google or “site:www.google.com”, and you will see these results in Bing. You can check if search engines index your homepage by typing your homepage after the “site” operator.
Getting your site on search engines
Although your website is in the index, the crawlers may miss some pages. Reasons they are not crawled or in the index can be:
- New site
- Not well-connected to other sites on the internet
- Crawlers cannot effectively crawl your site due to the design of your site
- You prevent or block the crawlers
- Your site violates the webmaster guideline for Google or Bing
Developing or optimising your site to become a Google-friendly website should help your site appear on search engines. Use Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to review a site with your website developers. If you specifically look for Bing, here is the Bing Webmaster Tools.
Submit your sitemaps to search engines
A sitemap is sort of a file to inform search engines about pages on your site. Let’s say you already have a website; you can submit the sitemaps to both Google and Bing to ensure that their crawlers can find your website.
Some sitemap generators that you can use are:
Stopping crawlers to crawl specific pages
In developing a website, you must prioritise your potential visitors. So, it would be best to hide particular pages that may be irrelevant for visitors from the crawlers. Doing so will help your site to only serve the most relevant result for visitors.
To do so, you can discuss adding a “robots.txt” file or use the noindex tag. Consult with your website developers and ask them to follow the best practices from the webmaster guidelines.
Mobile-friendly site
As the leading search engine, Google is leaning toward mobile devices. They prioritise a mobile version instead of a desktop version in indexing a site. Optimise your site to increase its mobile-friendliness by doing:
- Responsive web design as recommended by Google
- Configure them to be indexed accurately
- Check your site with mobile-friendly test from Google
Organise your site
An organised site helps crawlers in collecting information on your site. Consider implementing recommended practices:
- Use https:// for your URL
- Structured directories
- Breadcrumb list
- Easy-to-access navigation page for visitors
- Simple and relevant URL
Visually-appealing search results
You do not have any worries regarding your site’s technical stuff because a team of proven website developers handles it. Still, you can go the extra mile to attract searchers to visit your site by improving your SERP appearance.
Make an eye-catching appearance by considering:
- Adding structured data markup
- Using the correct markup
- Check and monitor the work through the Rich Results test
In short, if you do not possess the abilities to do technical SEO, it is always best to discuss this part with your website developers.
Following recommended practices from Google Webmaster Guidelines or Bing Webmaster Guidelines in creating and maintaining a website can help you in the long run. For example, when search engines implement new algorithm changes or avoiding penalties due to violation of rules.
Beware with linking
When you link your site to other sites through hyperlinked text (anchor text), it will deliver your site’s reputation to them. Consider using the nofollow tag if you have to link to another page outside of your site.
Crawlers will see the nofollow tag as a signal that your site does not have affiliation with linked sites outside of your domain. That way, your site will not share its reputation with the linked sites.
For instance, the nofollow tag is helpful in:
- Accidentally link your site to a spammy site
- Eliminating comment spam because spammers can take advantage of comment or message board on your site to generate a link to their site
Optimising on-page SEO for visitors and crawlers ✍

On-page SEO refers to optimisations of content on a website that you do within your site’s back end or content management system. The optimisations should help in the usability and user experience of your site. In return, your site could experience increased visibility on search engines.
On-page optimisations can be done without guidance from website developers.
Unique and relevant page titles
Write a unique and relevant title for every page on your site. The unique title helps visitors and crawlers to understand the topic of a page. So, the best practice is to avoid copying and pasting your title.
The dos:
- Write an original and relevant title
- Take time to write a unique title for every page
- Choose a brief title
- Pixel width decides how titles are shown on the SERP, but a good rule of thumb for your title is 50-60 characters
The don’ts:
- Using a single title for all your pages
- Irrelevant title
- Using default or template name (page 1, page 2, untitled)
- Lengthy title
- Keywords stuffing
A tip: you can use a tool, such as a snippet optimisation tool, to see how your title would look like on SERP.
Describe your pages on meta description
A meta description is a descriptive sentence(s) that users see on search engines. The description that you see is either generated by search engines or written by the pages’ owners.
Yes, search engines, such as Google, admit that there is a big chance they will not show the meta description that you already wrote to their users. Quoting directly from them,” Google may choose to use a relevant section of your page’s visible text if it does an excellent job of matching up with a user’s query.”
However, the best practice is you still have to provide a unique and descriptive meta description. Doing so could minimise the risk of Google picking irrelevant texts for your pages on the SERP.
The dos:
- Meta description must be unique
- Write a brief and compelling description for a page
- Google does not define minimal or maximal length, but you should aim for it to be long enough, such as between 50-160 characters
- Use the snippet optimisation tool to find out whether your description is too short or not; Google might not show the full description if it is between 155-160 characters
The don’ts:
- Write an irrelevant or generic description
- Unnecessary keywords stuffing
- Copying the content of a page and pasting it as a meta description
- Using the same description for all pages
Headings for important text
On a page, headings inform visitors and crawlers about topics. For instance, a page title is usually formatted as heading 1 (H1). An organised and proper usage of headings can improve the user experience of a page.
The dos:
- Only use one H1 for every page
- Use headings H2, H3, and so on sparingly
- Headings and their subheadings can serve as main points and sub-points for the content on a page
- The best practice is to position H1 after the header of your website
The don’ts:
- Excessive headings
- Lengthy headings
- Unorganised headings, such as jumping from H2 to H4
Attract visitors with exciting and valuable content
You can attract potential visitors to a site by providing compelling content. Great content can generate a real buzz when visitors discuss it on their blog, social media, forums, and other channels. Some examples of content on a site can be:
- Product pages
- Blog posts
- Articles
- Guides
- Videos
- Infographics
Keyword research
Keywords or phrases are the basis of search engines. You can find the estimated volume of searches for them on tools, such as Keyword Planner. Find and identify keywords related to your site and optimise each page from your keywords list.
When you plan to write or create content that may help SEO-wise, keyword research can be handy to find out what people are searching for that may be relevant to your site.
Content marketing
A lot of businesses utilise content marketing to gain organic traffic for their site. When you go down this route, remember the following.
The dos:
- Create content for visitors—not search engines—must be on top of your mind
- Fresh and unique content
- Easy-to-read text
- Organise your content, such as usage of headings and subheadings, provide more pictures for long-form articles
The don’ts:
- Duplicating content from other sites
- Duplicate or near-duplicate content within your site
- Hard to read content, such as many spelling or grammatical errors on a blog post
- Unnecessary keywords stuffing resulting in an awkward text to read
Optimise images on your site
A well-optimized image could improve the usability of your site. For instance, a small file size will reduce the loading speed of a page. In turn, this will make your visitors stay on your page.
Additionally, you also have to provide alt text on your images. Alt text helps search engines to understand your content better.
Consider implementing the following best practices when using images on your site.
The dos:
- Use optimised images with a file size of less than 300KB per image
- Write brief and descriptive filenames
- Descriptive text for alt text of images
- Use formats supported by browsers, like JPEG, PNG, GIF, WebP, and BMP
The don’ts:
- Images with big file size
- Generic or lengthy filenames
- Copying and pasting sentences into alt text
- Filling alt text with keywords
- Lengthy alt text
E-A-T rule from Google
E-A-T stands for expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. When visitors visit your website, they should trust your website. Start building a site with a good reputation by providing information, e.g., the “About Us” page, clear privacy and the user policy, or information about the team behind the service offered.
When your site offers a service or product, customer service information and a detailed frequently asked questions (FAQ) page is a must-have for you.
If there is a financial transaction on your site, implement appropriate technologies to ensure safe and secure payment.
For the expertise part, gain credibility by assigning people with appropriate expertise to produce or edit your site’s content. For instance, if you manage a dental clinic site, your writer must write an article sourced from reputable medical journals. Then, the dentists should verify whether the information is correct and edit it when necessary.
If more and more visitors feel comfortable digesting the content you provide, the better the authoritativeness/popularity of your site will be. Hence, the Search Engine will rank your website better.
Avoid intrusive advertising placement
Bad ad formats can do more harm than good. If a site uses advertisements to gain ad revenue, consider giving a better experience for your visitors. Never consider ads that could distract visitors when they check your content. Intrusive advertising format on a page can be:
- Pop-up ads
- Large sticky ads
- Ads with countdown
- Auto-playing video ads
Anchor text
When you browse a site, have you ever seen a clickable text that links you to another page on a site or directs you to an external site? That hyperlinked text is known as anchor text.
The following is an example of anchor text.
The dos:
- Brief and descriptive
- Related with the linked page
- Visitors can identify anchor text quickly so they will not miss it or, worse, accidentally click it
The don’ts:
- Generic, e.g., “click here” or “read this page”
- Too many keywords for the anchor text
- Styling of a site that makes anchor text looks like a standard text
- Writing page URL as an anchor text unless you are promoting a new site
Internal and external linking
Linking with anchor text must serve a purpose that helps visitors, e.g., recommending a page related to the current content accessed by them. For crawlers, good linking can help them understand your page better.
In SEO, there are two link types. They are internal links and external links. An internal link is a link to direct visitors to another page within the same domain. In simpler terms, it is linking one page to another related page within your site.
An example of an internal link, e.g., you should read this article to understand what SEO is.
On the other hand, an external link is an anchor text to link a page to another page outside your site. When another site links its page to yours, it is also an example of the external link.
The dos:
- Consider using nofollow tag for external linking
- Linking to a related topic
The don’ts:
- Off-topic
- Unnecessary linking
Promoting your website through off-page SEO 🔊
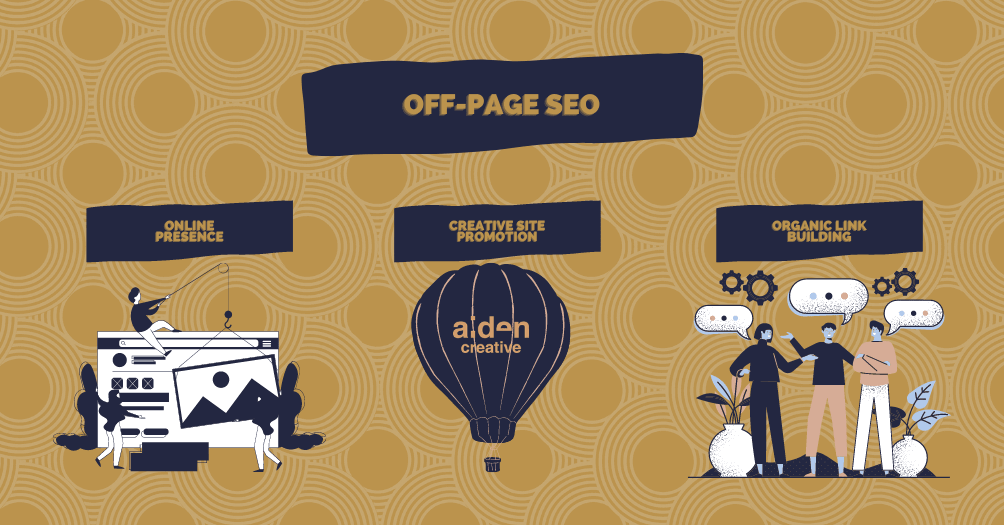
Hooray! You have done all the smart and hard work to improve your site performance by optimising your site’s technical and on-page SEO. They are standard optimisations for all the websites in the market.
Anyway, you can still improve it by doing off-page SEO. In simpler terms, off-page SEO means optimisations that you do outside of your site.
When people discover and enjoy your content, they will not hesitate to share your content/site. This share might help your site get traffic from other sites.
Nonetheless, you still want to promote your site. Google pointed out that promoting your site can be rewarding as long as you do not violate their guidelines. Some examples of bad practices are buying or selling links or using bots to generate links to your site. These practices could harm the reputation of your site or even get a penalty from them.
The dos:
- Create and update a business listing through Google My Business or Bing Places for Business
- Establish an online presence for your site through social media, and interact with relevant users through that channel could help to build an audience for your site
- Build link organically, e.g., link building case study
- Using newsletter to inform subscribers of new content on your site to bring constant traffic from your loyal subscribers
- Getting creative with offline promotion, e.g., put the URL of your homepage on the uniform of your employees
The don’ts:
- Promoting every new, thin content on your site
- Involved in link schemes to manipulate a site’s ranking
- Link spam
- Link exchange
Since we discuss social media, you may wonder how social media impacts SEO.
So, does Google take account of social media?
Gary Illyes, Google’s Webmaster Trends Analyst, said no. In other words, likes or engagements will not directly impact your site’s ranking.
Still, an online presence through social media may help people to discover your site.
Evaluation time for your site
Continually monitor and evaluate your site to see how they perform on search engines. You can start with free tools from major search engines, such as Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
Overall, these are some things you can check there:
- Monitor the performance of your keywords
- Identify crawling issues
- Find titles and meta descriptions that can be optimised
- Get top search queries that lead visitors to your site
- Helping in technical SEO, e.g., analyse robots.txt or submit sitemaps
Recap on how to optimise in SEO best practices 📝
All in all, SEO optimisation revolves around performing small changes, leading to noticeable improvements for user experience and your site’s organic performance. Some key points to optimise your site for search engines are:
- Build and optimise a site that can be crawled and indexed by crawlers
- Ensure the mobile friendliness of your site
- Follow the recommended practices for on-page SEO
- Avoid involvement in link schemes or purchasing links
Always keep in mind that SEO takes time; continuously evaluate and monitor your site’s performance.






